Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) have become a popular choice for individuals seeking to save for their retirement. This tax-advantaged investment account offers a range of benefits and flexibility, making it an attractive option for those aiming to secure their financial future. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of IRAs, exploring what they are, how they work, and the benefits they provide.
What Is an IRA?
An IRA, or Individual Retirement Account, is a type of savings account that allows individuals to set aside money for retirement on a tax-deferred basis. This means that the contributions are tax-deductible, and the earnings on the investments are not subject to taxes until withdrawal. IRAs are designed to help individuals build a retirement nest egg, providing a source of income in their golden years.
There are several types of IRAs available, each with its own set of rules and regulations. The two main types are:
- Traditional IRA: Contributions are tax-deductible, and the earnings on the investments grow tax-deferred. Withdrawals are subject to taxes and penalties if taken before age 59 1/2.
- Roth IRA: Contributions are made with after-tax dollars, and the earnings on the investments grow tax-free. Withdrawals are tax-free if taken after age 59 1/2.
How Does an IRA Work?
To understand how an IRA works, let’s break down the process into its key components:
- Opening an IRA Account: You can open an IRA account with a financial institution, such as a bank, credit union, or investment firm. You’ll need to provide personal and identification information, as well as meet the eligibility requirements.
- Contributing to an IRA: You can contribute to an IRA with after-tax dollars or tax-deductible dollars, depending on the type of IRA you choose. The contribution limits for 2023 are:
- Traditional IRA: $6,000 ($7,000 if you are 50 or older)
- Roth IRA: $6,000 ($7,000 if you are 50 or older)
- Investing in an IRA: Once you’ve contributed to an IRA, you can invest the funds in a variety of assets, such as:
- Stocks
- Bonds
- Mutual funds
- Exchange-traded funds (ETFs)
- Real estate investment trusts (REITs)
- Earnings and Growth: The investments in your IRA will grow over time, earning interest, dividends, and capital gains.
- Withdrawals: When you reach retirement age, you can withdraw the funds from your IRA to support your living expenses. If you withdraw before age 59 1/2, you may be subject to penalties and taxes.
Benefits of an IRA
IRAs offer a range of benefits, making them an attractive option for individuals seeking to save for retirement. Some of the key benefits include:
- Tax Advantages: Contributions to a traditional IRA are tax-deductible, and the earnings on the investments grow tax-deferred. Withdrawals are subject to taxes and penalties if taken before age 59 1/2.
- Compound Interest: The power of compound interest can help your IRA grow significantly over time, providing a substantial source of income in retirement.
- Flexibility: IRAs offer flexibility in terms of contribution amounts, investment options, and withdrawal rules.
- Portability: IRAs are portable, meaning you can take them with you if you change jobs or move to a different location.
- Protection: IRAs are protected from creditors in the event of bankruptcy.
Types of IRAs
There are several types of IRAs available, each with its own set of rules and regulations. Some of the most common types of IRAs include:
- Traditional IRA: Contributions are tax-deductible, and the earnings on the investments grow tax-deferred. Withdrawals are subject to taxes and penalties if taken before age 59 1/2.
- Roth IRA: Contributions are made with after-tax dollars, and the earnings on the investments grow tax-free. Withdrawals are tax-free if taken after age 59 1/2.
- Rollover IRA: A rollover IRA is used to transfer funds from a 401(k) or other employer-sponsored retirement plan into an IRA.
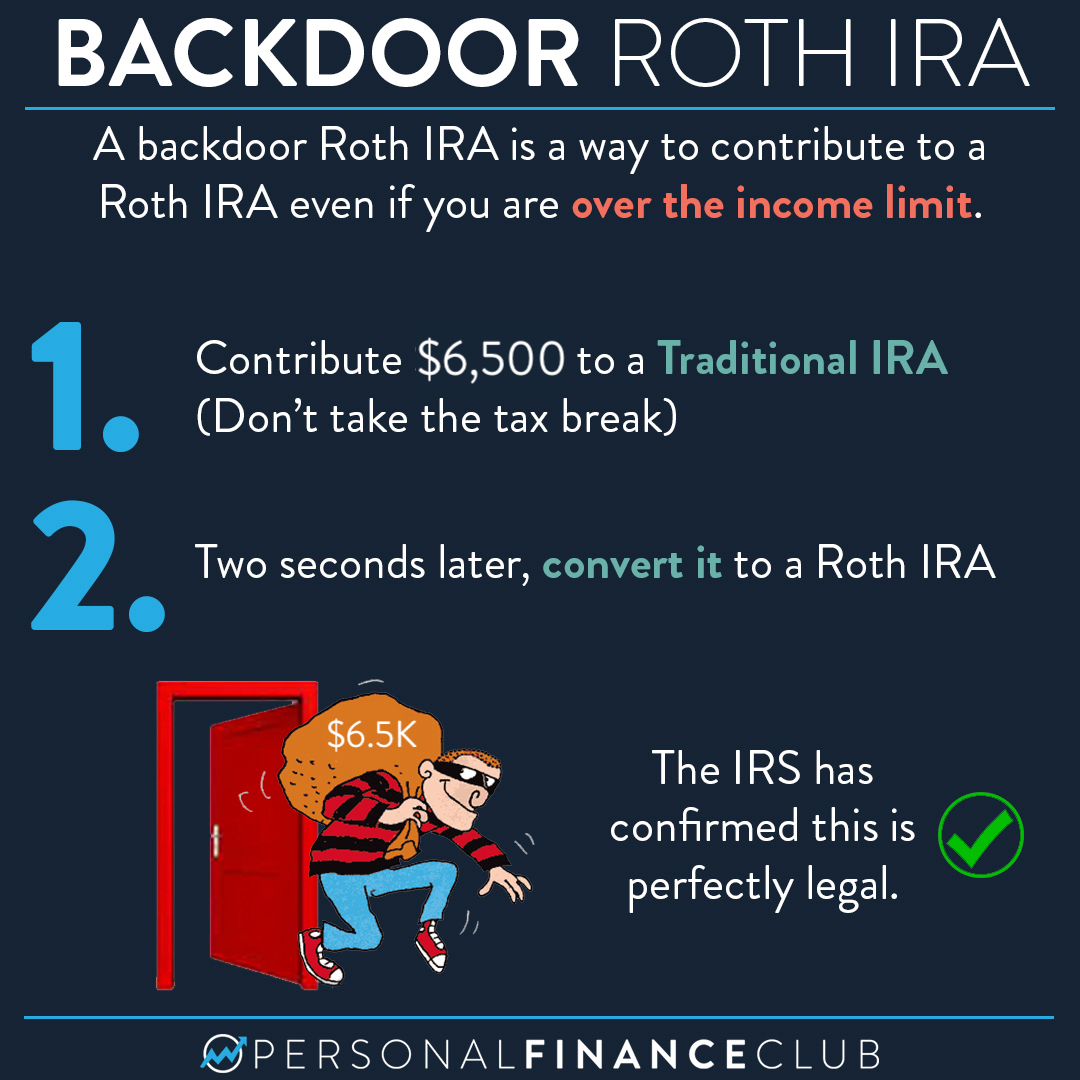
- Conversion IRA: A conversion IRA allows you to convert funds from a traditional IRA to a Roth IRA, subject to income limits and other rules.
Eligibility Requirements for an IRA
To be eligible to open an IRA, you must meet certain requirements. Some of the key requirements include:
- Age: You must be at least 18 years old to open an IRA.
- Income: You must have earned income, such as a salary or wages, to contribute to a traditional IRA. Roth IRA contributions have no income limits.
- Residency: You must be a U.S. citizen or resident alien to open an IRA.
- Tax Filing Status: You must file a tax return with the IRS to contribute to a traditional IRA.
Investment Options for an IRA
IRAs offer a range of investment options, allowing you to diversify your portfolio and optimize your returns. Some of the most common investment options for IRAs include:
- Stocks: Stocks represent ownership in a company and can provide long-term growth potential.
- Bonds: Bonds represent debt securities, offering regular income and relatively low risk.
- Mutual Funds: Mutual funds are diversified investment vehicles that pool money from multiple investors to invest in a range of assets.
- ETFs: ETFs are exchange-traded funds that offer diversification and flexibility.
- Real Estate: Real estate investment trusts (REITs) offer a way to invest in real estate through an IRA.
Withdrawal Rules for an IRA
Withdrawal rules for IRAs vary depending on the type of IRA and your age. Some key withdrawal rules include:
- Traditional IRA: Withdrawals are subject to taxes and penalties if taken before age 59 1/2.
- Roth IRA: Withdrawals are tax-free and penalty-free if taken after age 59 1/2.
- Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs): Beginning at age 72, you must take RMDs from a traditional IRA each year.
Contribution Limits and Taxes on IRAs
Contribution limits for IRAs vary depending on your age and income. Some key contribution limits and taxes on IRAs include:
- Traditional IRA: Contribution limits for 2023 are $6,000 ($7,000 if you are 50 or older).
- Roth IRA: Contribution limits for 2023 are $6,000 ($7,000 if you are 50 or older).
- Taxes: Contributions to a traditional IRA are tax-deductible, and the earnings on the investments grow tax-deferred. Withdrawals are subject to taxes and penalties if taken before age 59 1/2.
Conclusion
IRAs offer a tax-advantaged way to save for retirement, providing a range of benefits and flexibility. Whether you choose a traditional IRA or a Roth IRA, investing in an IRA can help you build a retirement nest egg and secure your financial future. By understanding the key components of an IRA, including contribution limits, investment options, and withdrawal rules, you can make informed decisions about your retirement savings.
Final Tips
- Start Early: Begin contributing to an IRA as early as possible to take advantage of compound interest.
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Spread your investments across a range of assets to minimize risk and optimize returns.
- Reinvest Dividends: Reinvest dividends to maximize your returns and avoid taxes.
- Consult a Financial Advisor: Seek the advice of a financial advisor to create a personalized retirement plan.
- Stay Informed: Stay up-to-date with IRS regulations and tax laws to ensure compliance and maximize your benefits.
By following these tips and understanding the key components of an IRA, you can create a successful retirement savings plan and secure your financial future.